Botox Injections in the Hackensack and Paramus, NJ area
To Reduce Horizontal Forehead Lines
Performing BOTOX® injections to treat horizontal forehead lines is relatively easy, and the result usually is quite satisfying. Treatment can include injections for glabellar frown lines when appropriate.
The frontalis muscle elevates the eyebrows and the skin of the forehead. The fibers of the frontalis are oriented vertically, and wrinkles of the forehead are oriented horizontally. The frontalis muscle originates on the galea aponeurotica near the coronal suture and inserts on the superciliary ridge of the frontal bone and skin of the brow, interdigitating with fibers of the brow depressors (ie, procerus, corrugator supercilii, orbicularis oculi muscle). The medial fibers usually are more fibrous than the lateral fibers, thus requiring less toxin for paralysis. Avoid total paralysis of the frontalis, since this is likely to cause brow ptosis and loss of expression. Injection too close to the lateral eyebrow can cause lateral eyebrow ptosis.
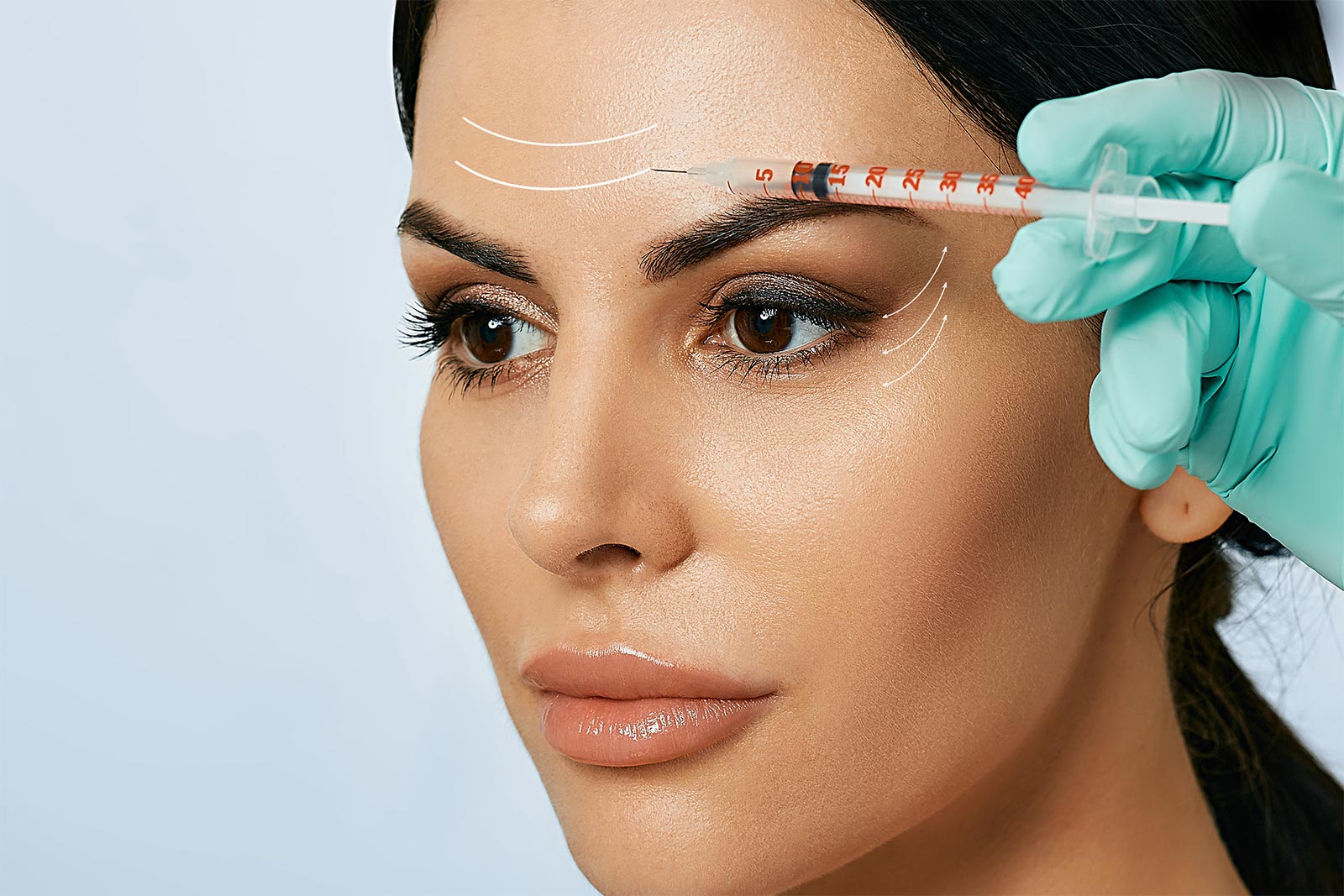
Botox Technique
Multiple injections of small amounts of toxin create weakness without total paralysis. Inject 3-5 sites botox on each side of the midline, usually using 2 units (1-3 U) per site. Separate sites by 1-2 cm. Choose an initial injection site approximately 1 cm above the eyebrow vertical to the medial canthus. Additional sites diverge laterally and upward to the hairline in a “V” configuration, often for a total of 3 sites. Additional sites (1-3) can be added in the midline or more laterally (1-2) depending on individual and clinical response.
If wrinkles extend to the temporal region, lateral injections can be performed. Use caution to prevent injecting lateral to the lateral canthus to avoid inhibiting temporalis function. Use caution when injecting patients in whom the hyper functional frontal lines support a ptotic upper eyelid.
Injections of the upper face and periocular region usually are performed with the patient seated, and the patient is asked to remain upright for 2-3 hours to prevent spread of toxin through the orbital septum.

